Monohydrate or creatine malate which one to choose?
The differences between creatine HCL supplements and creatine monohydrate supplements are not something you can spot with the naked eye — the differences between these two types exist at a molecular level. While physically, creatine HCL supplements and creatine monohydrate supplements look basically the same, they have major differences when.. The difference is, these have gotten positive feed back and do work! Tri is the more absorbent and soluble of the two. Tri Creatine Malate is a compound of molecules created from malic acid and creatine. Tri Malate has 3 monohydrate molecules attached and Di Malate has 2.

Honolulu,HI Local Nutrition supplement store/Supplement Review Difference between Creatine HCI

Creatine Supplement Monohydrate Side Effects Benefits Workout Supplements For

Creatine Supplement Monohydrate Side Effects & Benefits Creatine, Creatine

Creatine HCL vs Monohydrate What The Data Says About Which Is Better Nutritioneering

How Are Creatine & Whey Protein Different From One Another?

Creatine vs Creatinine Difference and Comparison

Creatine and Whey Protein Differences? Should You Take Both?

creatine monohydrate vs creatine HCL
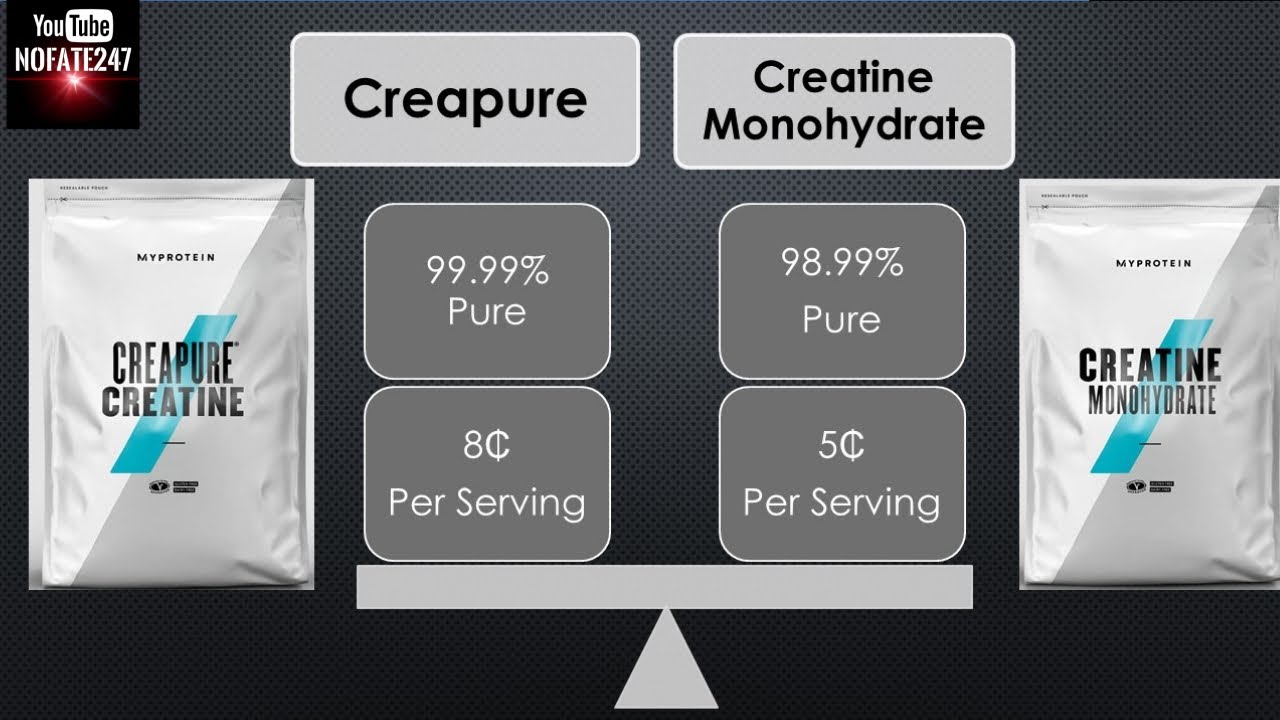
Difference Between MyProtein Creapure and Creatine Monohydrate Sunday Supplement Review YouTube

Creatine Monohydrate vs HCL Which is Best? in 2022 Creatine, Creatine monohydrate, Creatine hcl

BCAAs vs. Creatine Which One For Muscle? Naked nutrition

Creatine HCL vs Monohydrate Which Is Better For You

Creatine Supplement Monohydrate Side Effects & Benefits Creatine, Creatine
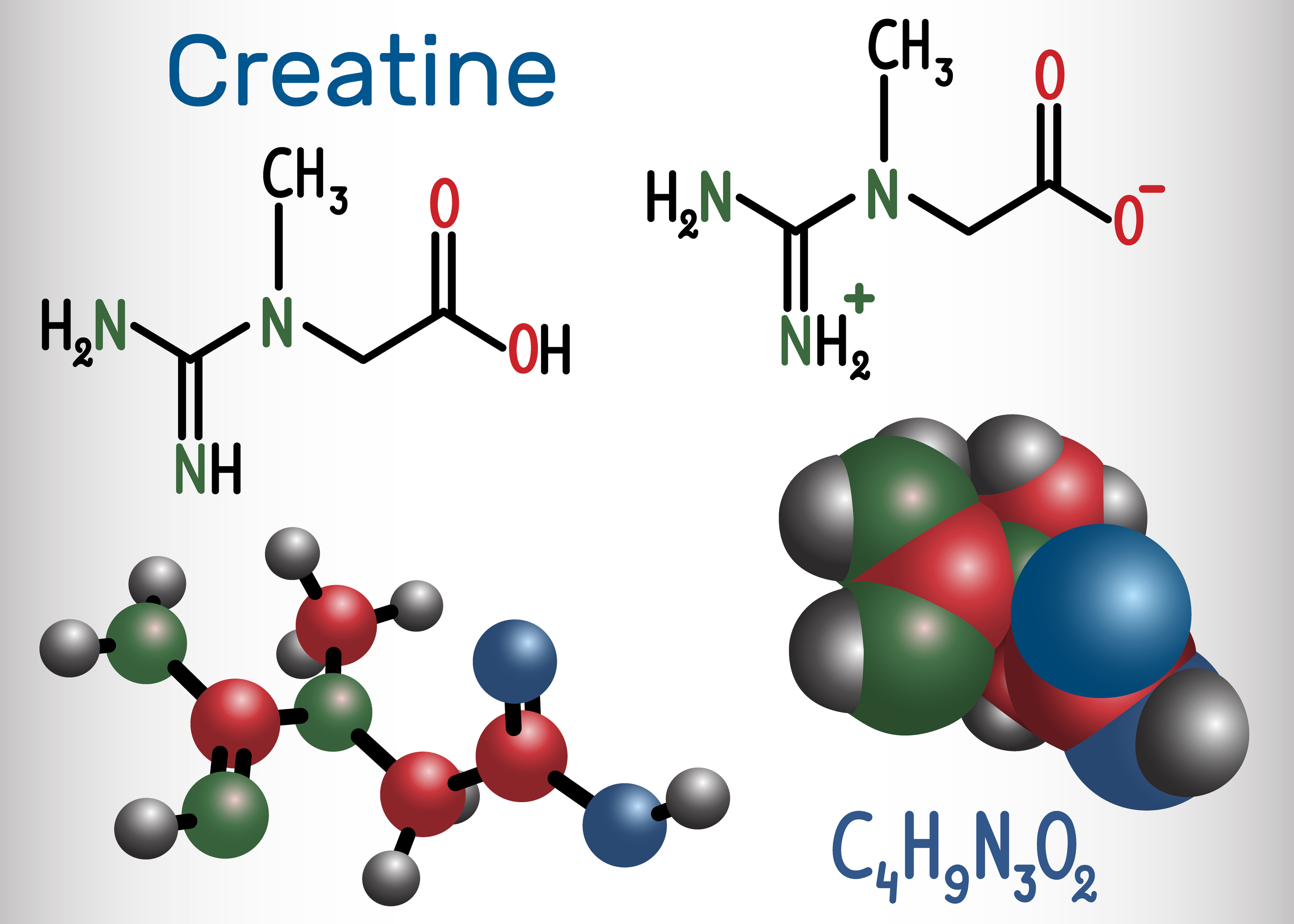
Monohydrate or creatine malate which one to choose?

Creatine HCL vs Creatine Monohydrate Which Is Best?

Creatine Monohydrate vs HCL The key differences Dr Workout

what is monohydrate vs micronized creatine what is difference and which is good YouTube

Creatine Monohydrate Vs Creatine Nitrate YouTube

Creatine Monohydrate vs. Creatine Hydrochloride YouTube

Differences between the various types of creatine detailed information backed up by studies
Creatine monohydrate crystallizes from water as monoclinic prisms that hold one molecule of water of crystallization per molecule of creatine . Subsequent drying of creatine monohydrate at about 100°C removes the water of crystallization yielding anhydrous creatine (100% creatine) . Creatine is considered a weak base (pKb 11.02 at 25°C) that.. A 2016 study measured the relationship between creatine nitrate and increased performance. It found no significant difference in lifting volume between nitrate and monohydrate groups, although people who took low-dose creatine nitrate supplementation did have an improved lifting volume compared to those who took a placebo.[3]


